MPPE (Macro Porous Polymer Extraction) is Veolia Water Technologies’ solution for removing hydrocarbons from pharmaceutical industry wastewater.
For HSE managers, wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) in pharmaceutical industries are increasingly seen as a new source of utilities and by-products. They are no longer just end-of-pipe treatment units for production waste before disposal - only receiving attention for maintenance to ensure compliance with discharge limits. Pharmaceutical wastewater is complex and varies from one production process to another, both quantitatively and in frequency (produced either continuously or in batches), as well as qualitatively (more or less biodegradable). Often, an audit of just the WWTP is proposed, to dissect the plant, investigate sources of toxicity and identify which sections require improvement of the existing treatment process. Laboratory testing on composite samples or pilot-scale systems is also conducted to ensure that the chosen treatment chain is the most optimised and efficient.
For instance, due to the toxicity of wastewater caused by certain compounds, residual APIs, or solvents used in production and synthesis, plant managers are constantly looking for improved technologies to upgrade existing systems. This is to avoid exceeding regulatory limits or to recover water, thereby reducing the need for well water or municipal supply. Space is often limited and energy consumption must also be kept low - ideally lower than current levels.
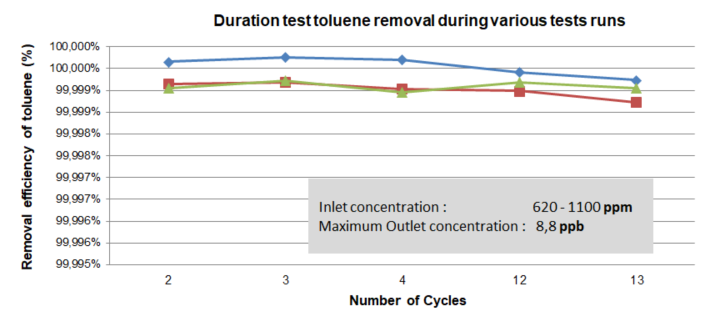
The presence of hydrocarbons in production depends on the process characteristics, but their use is widespread in R&D labs, biotech and API synthesis processes. In general, the pharmaceutical industry regularly uses over 30 solvents, including chlorinated solvents, dichloromethane for vitamin and antibiotic extraction, ethanol and methanol, polar solvents like acetone, GMP-grade IPA for oral solid preparation or in disinfectants and skin creams, as well as aromatic components like BTEX (e.g., toluene), with which MPPETM systems have achieved 99.9% removal efficiency. Discharge limits for these substances are stringent and are likely to face even more scrutiny in the future. Additionally, hydrocarbons are among the first wastewater substances targeted to align with corporate sustainability goals and principles.
A common treatment solution for hydrocarbon-contaminated wastewater is distillation columns, but these lead to high operating expenses due to energy consumption and require periodic cleaning that disrupts service continuity. And so, there's a need for more efficient and sustainable alternatives.
MPPE™ and the Extraction Process
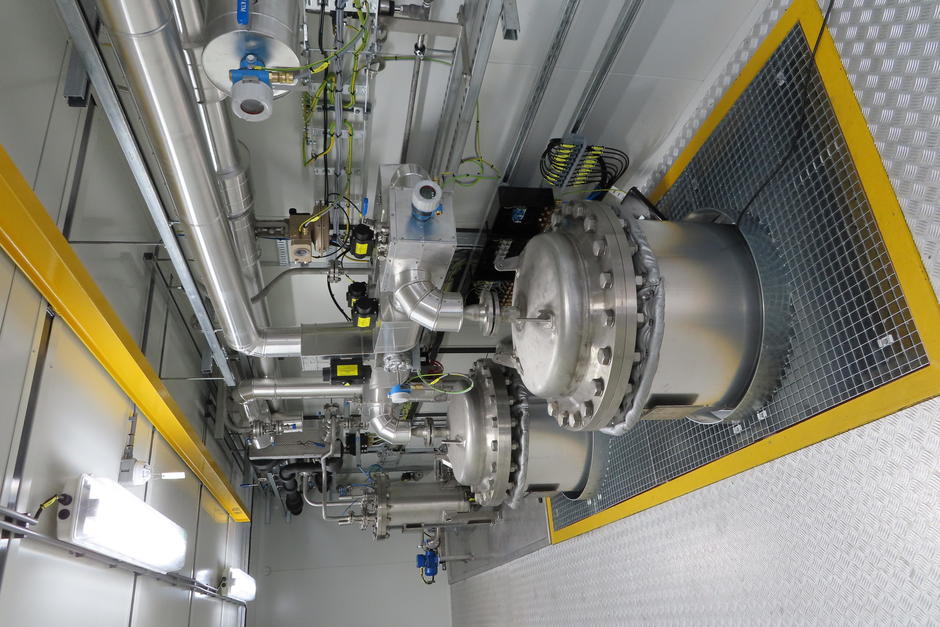
Veolia Water Technologies’ MPPETM (Macro Porous Polymer Extraction) technology offers a high-efficiency solution for removing dissolved and dispersed hydrocarbons from wastewater. This is an automated process, requiring minimal operational resources, no use of chemicals and it generates neither sludge nor waste gases. It uses a hydrocarbon-affine liquid fixed within a bed of porous polymer beads. When wastewater passes through this bed, hydrocarbons migrate from the aqueous phase into the extraction liquid. The purified water can then be further treated, reused or discharged.
When the extraction liquid becomes saturated with hydrocarbons, it is periodically regenerated by heating with low-pressure steam at 112°C. The hydrocarbons are then condensed and removed in liquid phase using a separator. Nearly 100% of hydrocarbons are removed. The system includes two MPPE process columns, enabling continuous operation through parallel extraction and regeneration. During regeneration of the first column, the wastewater stream is diverted to the second extraction bed, ensuring uninterrupted treatment.
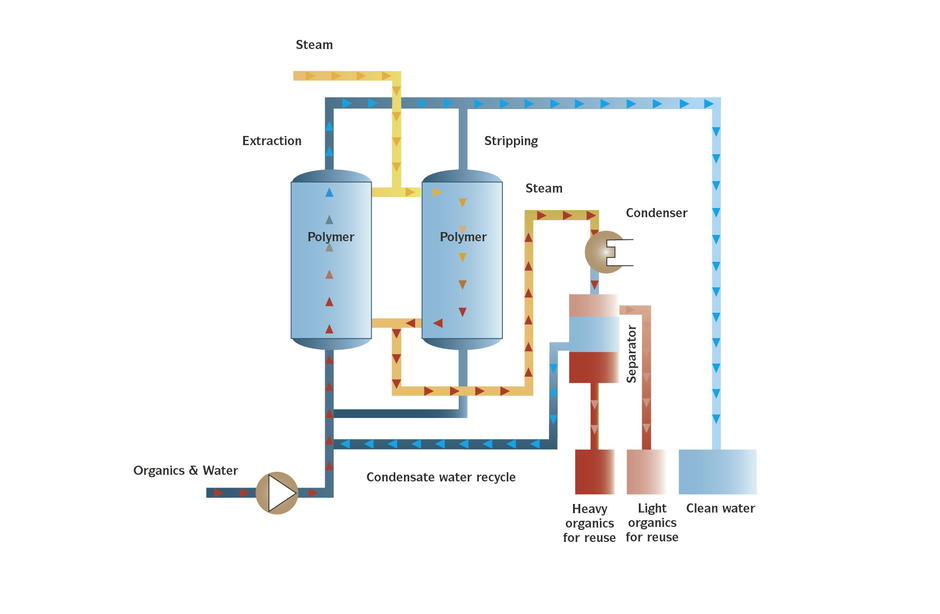
MPPE technology also allows control over removal efficiency by adjusting the amount of filtering media in the columns.
For polar compounds such as acetone, IPA, MEK, MTBE, THF, phenols, a more specific type of filtering media is used, while maintaining the same operating principle. This enables the removal of a wider range of hydrocarbons.
Key Factors for MPPE™ Applications
The success factor of MPPE™ technology lies in its ability to remove the most complex substances from industrial wastewater. These are the most toxic compounds that are not absorbed in conventional biological treatment stages. Removing these substances allows for subsequent biological treatment or additional steps to reuse water on-site. Moreover, concentrating and removing the most toxic substances - by a factor of up to 200 - significantly reduces the volume and cost of third-party disposal treatments.

In terms of energy consumption, an MPPETM system uses only 10–20% of the energy required by a conventional distillation system. But let’s look at further advantages.
Though typically used to remove hydrocarbon solvent traces, MPPETM’s high recovery efficiency also makes it suitable for extracting other high-value compounds from wastewater, which can then be reused in pharmaceutical processes. There have been cases where recovered solvents were reused directly as extracted from the MPPETM system.
Another important factor is reliability. Distillation columns are prone to fouling and when this occurs, the column must be cleaned with solvents. During this time, the distillation system is out of service, resulting in process inefficiencies - an issue avoided with MPPETM systems.

Case Study - Scandinavian Plant
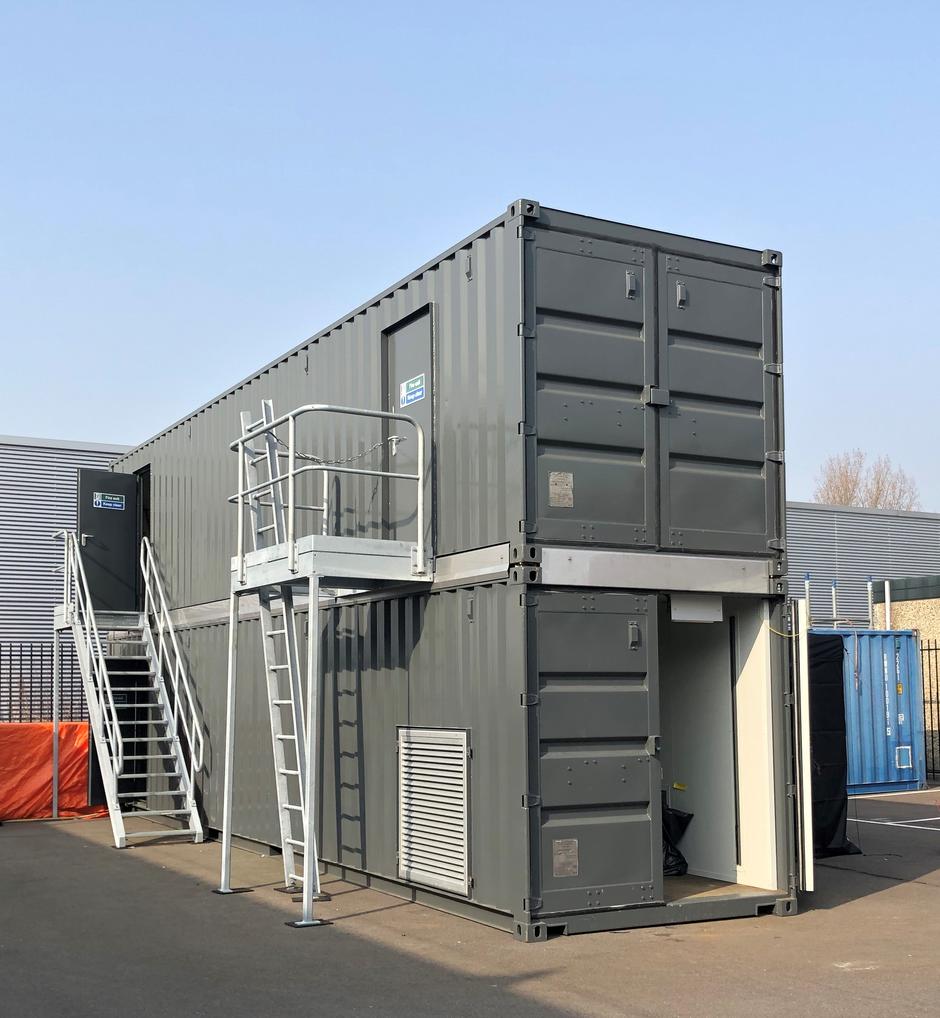
On request, we can provide a case study from a pharmaceutical plant in Scandinavia that used a conventional distillation column in its WWTP. Wastewater treatment was frequently interrupted due to fouling in the distillation towers. Energy consumption was also very high, prompting the company to seek better alternatives. During plant expansion, Veolia Water Technologies' MPPETM solution was considered. Through lab-scale pilot testing, attended by the client, Veolia was able to demonstrate improved process efficiency and energy savings with MPPETM technology. The plant was then implemented using a modular container solution, saving space near the site’s tank farm.
Hydrocarbon Recovery
MPPETM is not only an energy-saving solution for treating hydrocarbon residues in pharmaceutical wastewater. Its efficiency also enables the removal of nearly 100% of the hydrocarbon solvents used in the industry. Water treated with MPPETM can then be further purified with downstream systems, which typically require low hydrocarbon levels.
This helps pharmaceutical companies achieve significant water savings in their processes and supports the recovery of valuable materials such as solvents and even specific high-value products, from the wastewater stream. Often, effectively treating even a single pollutant in the wastewater flow allows MPPETM to solve a significant portion of the wastewater issues faced by pharmaceutical operations.
Ultimately, the MPPETM process enables pharmaceutical companies to ensure business continuity by maintaining environmental compliance of their processes and projects - both now and in the future.
Want to learn more about our pharmaceutical wastewater treatment solutions?
.png)


